Introduction
Key Takeaways
- CNC turning is a highly precise subtractive manufacturing process that produces cylindrical parts by removing material from a rotating workpiece using a stationary cutting tool.
- Key components of CNC turning machines include the spindle, chuck, tool turret and control panel, all of which play crucial roles in ensuring precision and efficiency during the machining process.
- CNC turning is versatile and widely used across various industries such as automotive, aerospace, medical and oil & gas, enabling the production of high-precision parts with tight tolerances and complex geometries.
What's CNC Turning
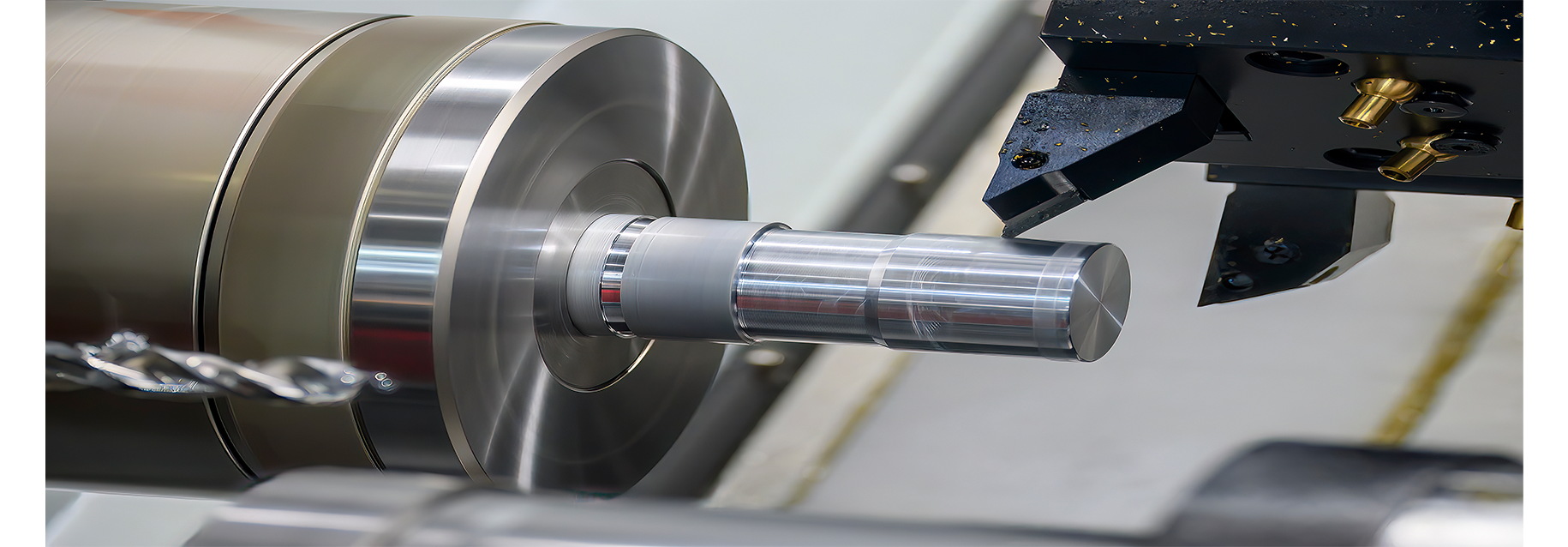
CNC turning is a subtractive process that makes cylindrical parts from various materials with high precision and speed. CNC turning is a subtractive technology where material is removed from the workpiece to get the desired shape.
In this process material is removed from a rotating workpiece using a stationary tool, to get complex geometries and tight tolerances. CNC turning has evolved from traditional lathe machines, modern CNC turning machines are advanced versions of these basic machine tools.
Understanding what is CNC turning and the process will give you more insight. Choosing the right material before starting the CNC turning process is key to get the precise and desired geometry.
CNC Turning Process
At its heart, CNC turning is a precise and efficient subtractive machining process. Unlike manual lathes which require constant operator control and limited automation and precision, CNC turning machines are automated and more accurate and repeatable. This process removes material from a rotating workpiece with a stationary cutting tool, unlike other machining processes where the tool rotates. This is the foundation of precision machining and allows for parts to be made with high accuracy and complex geometries required for industries with tight tolerances.
The CNC turning machine consists of:
Spindle:
turns the workpieceChuck:
holds the workpiece in placeCutting tools:
engage with the rotating material to cut out the desired shapes and dimensionsTool holders:
holds the cutting tools and CNC lathe machine
These components allow for various machining operations, such as turning, facing and boring to shape and finish the workpiece. These components work together to achieve precision machining. This harmony of components is what CNC turning is all about.
During the CNC turning process the workpiece rotates around a fixed axis, which is a big difference from other machining processes that may use multiple or moving axes.
How CNC Turning Works

The journey of a CNC turned part is:
- A CAD file is created.
- The CAD file is converted into a CNC program.
- The CNC program is loaded into the machine.
- The machine spins the workpiece at high speeds.
- A tool moves into position to remove material.
During the CNC turning process the workpiece rotates around its axis while the cutting tool, controlled by computer numerical control (CNC) technology, moves along specific paths to remove material and shape the part on a cnc machine during the cnc machining process. A single point cutting tool is used in CNC turning to achieve precise material removal and produce various workpiece geometries.
CNC turning can do multiple operations including different turning operations and machining operations. These operations are:
- Facing
- Straight turning
- Grooving
- Threading
- Boring: This process not only ensures accuracy but also efficiency and consistency in producing complex parts.
Key Components of CNC Turning Machines
- Headstock
- Tailstock
- Spindle
- Chuck
- Lathe bed
- Carriage
- Tool turret
- Tool post
- Cross slide
- Control panel
The tool post holds and locates the cutting tools, for quick tool changes and precision machining. The cross slide allows for movement of the cutting tool perpendicular to the axis of rotation, for facing and other precise cutting operations.
Each part has a job to do in the CNC turning process, to hold the workpiece, rotate it and shape it.
Let's look at each of these parts, starting with the headstock, tailstock and spindle.
Main Parts: Headstock, Tailstock and Spindle
The headstock is on the left side of the CNC lathe and contains the main drive and powers the spindle. The spindle is a critical part and rotates the workpiece at high speed so the cutting tool can remove material precisely. The chuck is attached to the spindle and holds the workpiece in place so it doesn't move during machining.On the other end of the lathe is the tailstock which provides additional support to the workpiece. Its functions are:
- Prevents deflection and keeps the workpiece aligned for longer or more flexible parts
- Holds drilling tools
- Allows operations that requires support from both ends of the workpiece.
Together the headstock and tailstock keeps the workpiece held and rotated accurately throughout the CNC turning process.
Tool Turret and Cutting Tools
The tool turret is a key component of the CNC turning machine and holds multiple tools and allows for quick tool changes, increasing machining time. This clamping device is essential for doing multiple turning operations without stopping the machine, reducing downtime and increasing productivity.
Tools mounted on the tool turret are for:
- Facing
- Straight Turning
- Grooving
- Threading
- Boring
Quick tool changes through the turret gives more flexibility.
This not only increases CNC turning efficiency but also allows for production of complex parts with complex geometry. A tool turret and specialized tools is what defines modern CNC turning machines.
Control Panel and Software
The control panel is the heart of the CNC turning machine, where the input device, display and other controls live. Operators input and edit the machining programs through the control panel, so the machine runs precise. The interface allows real time adjustments, so it's critical for CNC turning.
The CAM (Computer Aided Manufacturing) software complements the control panel by programming and managing the CNC turning. CAM software takes the CAD design file and converts it to G-code, the machine control unit reads the G-code and tells the machine what to do. This software and hardware integration makes the CNC turning process precise and automated, reduces human error and increases overall productivity.
Types of CNC Lathes
CNC lathes come in many forms, each designed for specific machining needs and production goals. The most common are horizontal CNC lathes, used for everything from simple turning to complex machining. Their horizontal design makes them perfect for high volume production and can handle all part sizes and shapes.
Vertical CNC lathes are designed for large, heavy workpieces that need extra stability and support. Their vertical design allows gravity to hold the workpiece, making them great for large bearings or heavy industrial parts.
CNC turning centers are the next evolution in lathe technology, combining the capabilities of CNC lathes with milling and drilling. These turning centers allow you to do multiple machining operations in one setup, reducing production time for complex parts.
For even more flexibility, multi axis CNC lathes add extra axes of motion, allowing for intricate and precise machining that would be impossible on standard lathes. These machines are necessary for parts with complex geometry and tight tolerances, supporting many industries and applications.
Types of CNC Turning Operations

CNC turning is a multi tasking process that encompasses many operations all done on a cnc turning center. With advanced turning capabilities cnc turning machines can handle many materials and high volume production and prototyping. These operations are used to machine the outside surface of a workpiece, outside diameters, different from processes like boring that machine the inside surface. The operations can be broken down into basic operations like facing and straight turning and advanced operations like grooving, threading, boring and turning. Each operation serves a purpose to produce parts with high precision and different shapes and sizes.
Let's get into the basic operations.
Basic Operations: Facing and Straight Turning
Facing and straight turning are the building blocks of CNC turning.
Facing:
- Trims the end of a part to length, perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
- Creates a flat surface at the end of the part, often a requirement for further operations.
- Gets the part aligned and ready for next operation.
Straight turning removes material along the length of the part to create a cylinder. This process uses a tool that runs parallel to the part to remove material evenly and get the desired diameter. This is used to create cylindrical parts common in many industries.
Taper turning is another basic process to create conical shapes with precise angles by varying the diameter of the part. This is used to create cones and tapered shafts that require precise fit.
Advanced Operations: Grooving, Threading and Boring
Advanced CNC turning operations like grooving, threading and boring take the process to the next level.
Grooving is:
- Cutting narrow cuts on the workpiece surface
- Adding features like slots or grooves
- External grooving or on the face of the workpiece depending on the requirement.
Threading involves precise tool movement to create helical grooves on the workpiece surface to form threads. This is critical for making threaded components which are used in fasteners and mechanical assemblies. Knurling is another operation where a special tool is used to create a pattern on the workpiece surface to provide better grip or decorative finish.
Boring is enlarging an existing hole to achieve the desired diameter and finish. This is important for making precise internal diameters which is required in components like bushings and bearings. All these advanced operations make CNC turning more versatile to produce complex functional parts.
Materials Used in CNC Turning
CNC turning is great for working with many different materials, so it's a good choice for many applications. Metals are the most common, with aluminum, steel, stainless steel, brass and titanium being popular for their strength, durability and machinability. These metals are good for making robust high performance parts across industries like automotive, aerospace and medical.
In addition to metals, CNC turning can machine plastics like nylon, polycarbonate and ABS. These materials are lightweight, corrosion resistant and adaptable, good for consumer products to specialized industrial parts.
The choice of material in CNC turning depends on the part requirements, mechanical properties, environmental resistance and cost. Understanding how each material behaves during the machining process is key to getting the best results, minimizing tool wear and ensuring the finished part meets all performance specs.
Advantages of CNC Turning
CNC turning has many advantages that make it the go to for high precision parts:
- Tolerances and high finish, meets specs.
- Faster production time than traditional methods.
- More efficient and cost effective.
CNC turning can handle many materials and complex designs, that's why we're exploring this further. But tooling costs can be a big part of the overall process.
High Precision and Accuracy
A big benefit of CNC turning is:
- Can achieve very tight tolerances, down to ±0.0001 inches.
- Precision required for applications that need exact dimensions and high finish.
- No human error for consistent results.
CNC turning is great for precision machining and cnc machining.
High precision allows for parts with complex geometry. This is important in industries like aerospace where parts must meet strict standards for safety and performance. Consistent tight tolerances makes CNC turning a must for quality and reliability in manufacturing.
Efficiency and Speed
Efficiency and speed are key. Here are:
- Choosing the right speed and feed rates to reduce machining time and extend tool life.
- Optimizing these to get faster production cycles and high volume production without compromising quality.
- Changing cutting tools through the tool turret which adds to the speed and efficiency of the process.
Besides reducing production time, CNC turning minimizes material waste, it's a cost effective process. Properly managing operational parameters like speed and feed rates will get you optimal cutting performance and extend tool life. All these will make CNC turning ideal for rapid prototyping and mass production.
Versatility and Flexibility
CNC turning is all about versatility and flexibility. It can handle a wide range of materials from metals like aluminum and steel to engineering plastics, it's adaptable to various industrial applications. This flexibility allows you to produce complex and intricate designs that traditional methods can't or won't. Whether it's simple cylindrical parts or complex geometries, CNC turning has the capabilities to meet your manufacturing needs.
Plus the ability to change between different cutting tools and operations makes CNC turning more flexible. This is perfect for job shops and manufacturers who need to produce various parts in small to medium batches. The combination of material versatility and operational flexibility makes CNC turning a must have in today's fast paced manufacturing world.
CNC Turning vs. CNC Milling
CNC turning and CNC milling are two fundamental processes, each with its own strengths and applications. CNC turning revolves around a rotating workpiece and a stationary cutting tool, while CNC milling uses a rotating cutting tool to shape a stationary workpiece.
Knowing the differences helps you choose the right manufacturing method for your needs. Explaining the key differences and applications for each process will clarify their uses.
Rotating Workpiece vs. Rotating Tool
In CNC turning, the workpiece is rotated around its axis. The cutting tool is stationary. This is perfect for making cylindrical parts as the rotating workpiece allows for uniform material removal along its length. CNC turning centers which are advanced versions of traditional CNC lathes often have automated tool changing, efficient chip removal and higher RPM's making them more versatile and efficient.
In CNC milling the workpiece is stationary and clamped to a bed while the cutting tool rotates to remove material. This process is good for making flat surfaces, intricate designs and complex geometries that require multi axis machining. The main difference between these processes is the mechanism of material removal, each has its own advantages depending on what you want to achieve.
Suitable Applications for Each Process
CNC turning is good for cylindrical parts like shafts, rods and bushings, common in automotive and aerospace. Its efficiency and ability to hold tight tolerances makes it ideal for mass producing engine components, transmission parts and other critical parts that require precise dimensions.
CNC milling is good for flat surfaces and complex designs like brackets, housings and complex geometries. Aerospace industry often prefers CNC milling for creating precision components with tight tolerances where multi axis machining is required.
CNC milling is versatile and can produce a wide range of products from jewelry to intricate automotive parts. By knowing the strengths of each process, manufacturers can choose the right process for their needs and get the best results in their production.
Industries Utilizing CNC Turning
Looking at CNC turning in these industries shows its versatility and impact on various manufacturing processes.
Automotive and Aerospace
In the automotive industry, CNC turning makes intricate components like pistons, cylinder heads, gears and shafts which are critical to vehicle performance. The precision and efficiency of CNC turning ensures these parts meet specifications, contributing to overall vehicle reliability and performance. It shortens production lead times and gets automotive products to market faster.
In aerospace, CNC turning produces critical engine parts from tough materials, ensuring safety and reliability in flight. Components produced using CNC turning include:
- Turbine blades
- Housings
- Landing gear parts CNC turning provides the precision and consistency required in this high risk industry. Producing components and complex lightweight components makes CNC turning key in aerospace manufacturing.
Medical and Oil & Gas
In medical, CNC turning produces parts for medical equipment such as surgical instruments, implants and diagnostic devices. Accuracy and finish are critical for medical devices to be safe and effective. Being able to work with various materials including biocompatible metals and plastics makes it even more applicable in medical.
Oil and gas uses CNC turning to produce robust parts like valves, pipes and fittings that can withstand harsh environments. Durability and precision is key to ensure equipment used in oil and gas exploration and production are reliable and safe. Meeting these industries demands proves CNC turning is versatile and critical in today's manufacturing.
CNC Turning Design Considerations
When designing parts for CNC turning there are several key factors to consider to ensure efficient manufacturing and good results. First and foremost is the material selection as this will affect machinability, tool life and the final properties of the part. The design should also consider the shape and features of the part to ensure they are compatible with the CNC turning machine and the tooling.
Tolerances and surface finish requirements must be specified based on the part function and industry standards. Too tight tolerances can increase machining time and cost so it's important to balance precision with manufacturability. Also designing for efficient material removal can reduce cycle times and tool life and make the process more cost effective.
Other considerations are the number of axes on the turning machine, the size and complexity of the workpiece and the type of machining operations required. By considering these factors early in the design process manufacturers can streamline production, reduce errors and get consistent good results.
Best Practices for CNC Turning
Exploring best practices will improve CNC turning performance and longevity.
Choosing the Right Tools
Choosing the right tools is key to successful CNC turning. When selecting tool inserts consider:
- The workpiece material, different materials require different cutting characteristics.
- The crystal orientation of coatings.
- The microstructure of coatings.
These will impact CNC turning tool inserts performance, wear resistance and machining costs.
Proper tool storage and handling is key to keeping tools in good condition and extending their life. Using condition monitoring systems will help predict tool wear and schedule replacements, reduce downtime.
Selecting and maintaining the right tools will optimise CNC turning for better efficiency and precision.
Speed and Feed Rates
Speed and feed is key to efficient CNC turning. Spindle speed, feed rate and depth of cut must be controlled for optimal cutting. These parameters affect the finished product and cutting efficiency and tool life.
Understanding and adjusting these operational parameters is crucial for high precision and minimal material waste. Proper management of speed and feed saves time and allows manufacturers to meet tight deadlines and increase production.
Fine tuning these parameters improves overall CNC turning performance.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability in CNC Turning
Like many manufacturing processes CNC turning has an environmental footprint of energy consumption, material waste and coolants and lubricants. The industry is adopting sustainable practices. Optimising machining parameters improves efficiency and reduces energy and material waste. Many manufacturers are switching to eco friendly coolants and implementing recycling programs for metal chips and scrap.
CNC technology is also advancing. Modern CNC turning machines are designed for higher efficiency with better tooling materials that extend tool life and reduce waste. By embracing these innovations and sustainable practices the CNC turning industry is minimising its environmental impact while maintaining high productivity and quality.
CNC Turning Costs
CNC turning costs are influenced by part complexity, material selection, volume and machining time. While the initial investment in CNC machines and tooling can be big, the long term benefits – increased precision, reduced labor costs and ability to hold tight tolerances – will pay off in the long run.
Complex parts with high surface finish can command premium pricing especially in industries where precision and reliability is key. To stay competitive manufacturers need to manage material, energy and labor costs and optimize processes to get the most out of it.
Investing in advanced CNC machines and high value added products will further increase profitability. By leveraging the strengths of CNC turning – ability to produce intricate parts with tight tolerances – manufacturers can be economic and stay competitive in the global market.
How We Can Help
Clarwe offers full CNC turning services to produce high quality prototypes and end use parts with fast turnaround times. Using the latest technology and strict quality control Clarwe can provide custom solutions for various industries, flexibility and precision in manufacturing.
Looking into the services and quality control shows why Clarwe is your go to partner in CNC turning.
Full CNC Turning Services
Clarwe offers full CNC turning services for all your manufacturing needs. Whether rapid prototyping or mass production Clarwe supports you from design to delivery, efficient and precise manufacturing. Our CNC turning solutions are tailored to each industry's specific requirements, high adaptability and flexibility.
With our advanced capabilities and state of the art equipment we can handle all materials and complex geometries, high quality precision machined components for our clients. Combining expertise and technology we can deliver reliable and cost effective CNC turning services for the manufacturing industry.
Quality Assurance and DFM Feedback
At Clarwe, quality is key. We test and inspect throughout the manufacturing process to ensure all parts meet the highest standards. X-Ray Fluorescence and Coordinate Measuring Machines check raw material properties and dimensions, so you get parts with tolerances as tight as ±0.005 mm.
We also provide Design for Manufacturability (DFM) feedback to help you optimise your designs for production efficiency and cost. You can request quality reports, including material certifications and dimensional inspection data, so you can see exactly what you're getting.
By controlling quality and DFM feedback we ensure every CNC turned part is precision and reliable.
Conclusion
In summary, CNC turning is a precise and efficient process that's crucial for producing high quality cylindrical parts. With its ability to achieve tight tolerances, reduce lead times and handle a wide range of materials, CNC turning is essential in many industries from automotive to aerospace and medical to oil & gas. The detailed explanation of CNC turning processes, machine components, operations and best practices shows how versatile and important this machining technology is.
As we've seen, the benefits of CNC turning are many, high precision, efficiency and flexibility. By understanding the difference between CNC turning and milling, manufacturers can choose the right process for their needs and get the best results. With comprehensive services and quality assurance from companies like Clarwe, manufacturers can get the best out of their CNC turning. Try CNC turning and open up new possibilities in precision manufacturing.
FAQ's about CNC Turning
What is CNC turning?
CNC turning is a subtractive machining process where material is removed from a rotating workpiece with a stationary cutting tool. It's fast and accurate.
What's the difference between CNC lathes and CNC turning centers?
CNC turning centers have automated tool changing, better chip removal and higher RPM's than traditional CNC lathes. So if you need more complex operations a CNC turning center may be the way to go.
How is CNC turning different from CNC milling?
CNC turning has a rotating workpiece and a static cutting tool, whereas CNC milling has the workpiece fixed and the tool spinning. This affects the types of shapes and features that can be produced by each.
What shapes can CNC turning produce?
CNC turning can produce cylindrical, oblong, conical, disk and polygonal shapes like hexagons and squares. This versatility allows for intricate designs and precise manufacturing.
In which industries is CNC turning used?
CNC turning is used in the automotive, aerospace, medical and oil and gas industries. These industries require precision machining for high quality components.

