
Introduction
Quick Facts
- CNC machining uses computerized controls to make parts with high precision and is a subtractive process, used in aerospace and automotive industries.
- The CNC machining process has 3 stages: design, programming with G-codes and M-codes and machining operations, all critical to making accurate parts.
- Benefits of CNC machining are precise control, high speed and consistent quality, drawbacks are high equipment cost and skilled operators.
What is CNC Machining
The true power of CNC machining is in its ability to make complex parts with high precision and speed, that's why it's used in industries from aerospace to consumer products. Understanding CNC machining will show you how this technology has changed modern manufacturing.
History of CNC Machining
CNC machining started in the 1940s with the first numerical control (NC) machines. These early machines paved the way for more advanced systems by using punched tape to control the machine. But it wasn't until the 1970s that a big leap forward happened when computers were added to the system. This is when the first CNC machines were born and could process data faster and more accurately than ever before and changed the manufacturing process.
During this time swiss screw machines also emerged as specialized lathes for high precision machining of small parts. Their movement capabilities allowed for tighter tolerances and better stability and were historically important for producing parts like watch screws and other parts that required concentricity.
The introduction of computers allowed for more advanced and versatile CNC machines that could do complex designs and complex machining. And that's where we are today where CNC is the backbone of modern manufacturing and producing high precision parts across all industries.
Key Components of CNC Machines
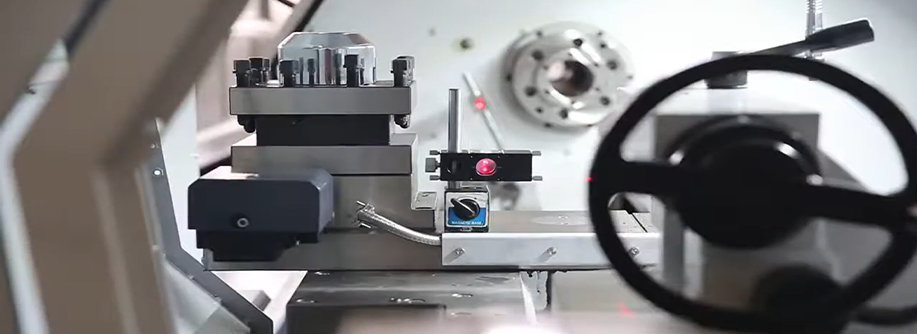
CNC machines are made up of many parts that work together to produce precise parts. At the heart of these machines are the computer controls that tell the machine where to move the complex machinery so each cut and shape matches the design. This combination of technology and cnc equipment allows raw materials to be turned into finished products with cnc machines. Understanding how cnc machines work is key to using them optimally.
Understanding how CNC machines are precise involves looking at the components: machine tools and control systems. Servo motors move the tools across the X and Y axes, exactly as the G-code says and in closed loop control systems. The tool spindle is another key component, holding the cutting tool and moving it along the X, Y and Z axes during machining. These are the building blocks of the CNC machining process, each one playing a critical part in the accuracy and efficiency of the operation.
Machine Tools
Machine tools are the workhorses of CNC machining, they do the actual cutting and shaping of the material. CNC machining uses various types of machine tools, including turning machines:
Lathes:
Stationary tools and rotating workpiece, good for cylindrical parts.
Milling machines:
Moving cutting tools and stationary workpiece, good for a wide range of milling operations.
CNC mill:
Advanced machine tool with rigid structure, multi-axis and automation, good for complex parts.
Cutters:
For specific operations in the machining process. Machine tool selection is key to efficiency.Besides lathes and mills, other machine tools like drills and cutters also play a big role in CNC machining. Each tool is selected based on the task requirement so that the final product meets the spec with precision.
Control Systems
Control systems are the brain of the brawn of CNC machines, telling the machine tools what to do. CNC machining has two types of position control systems: open-loop and closed-loop. Closed-loop is better as it gets feedback and can correct errors and have precise control of the machining process. Open-loop is simpler and used when the forces and speeds are minimal.
In CNC programming systems a code generator is used to generate the control code that runs the machine and makes it accurate and efficient.
The transition from numerical control to CNC was in the 1970s when computers were introduced. Analog and digital computers played a big role in this evolution and allowed for more sophisticated and accurate control of the machining process.
The CNC Machining Process

The CNC machining process is a precise process that can be broken down into three main stages: design, programming and machining operations. Each stage is critical to ensure the final product meets the required specifications. The cutting process starts with the creation of a computer aided design (CAD) model which is the blueprint of the part to be manufactured. The cnc milling process is part of these machining operations.
Once the CAD model is created, a machining program is generated from the CAD model and then converted into a CNC program using G-codes and M-codes which guide the machine's movements and operations. This machining program is run by the CNC milling machine to automate the manufacturing process with minimal human intervention.
The final stage is the running of the CNC program where the machine removes material to shape the part according to the design. Feedback systems and precise motors ensure each movement is precise and results in a high quality finished product while maintaining the optimal feed rate.
Design and CAD Model Creation
First we create a CAD model using CAD software to design 2D or 3D models for CNC machining. The CAD file is then converted into a machine readable format to create digital manufacturing programs. CAD and CAM software is used to create detailed drawings of the part to be manufactured. These drawings are then translated into computer aided manufacturing cam code which the CNC machine will use to run the machining operations.
Before you engage a CNC service provider you need to define your project specifications such as materials, tolerances and surface finishes. Careful consideration of these factors will ensure the final product is the shape and function you want.
Also designing parts without undercuts can make them more manufacturable and reduce production time on flat surfaces.
Programming with G-codes and M-codes
Programming is a key part of the CNC machining process using G-codes and M-codes to talk to the machines. G-codes deal with the tool parameters like movement and speed, M-codes deal with tool changes and other secondary functions. Pre-programmed software executes the instructions generated from the design and automates the process for efficient and precise manufacturing. CNC programs are the set of instructions generated from CAM software that tells the machine how to make the part including tool movements, spindle speed and tool changes. Precision in cnc programming and computer programming is crucial as it determines the machine's capabilities and each cut is made accurately.
After you input the CNC program, a test run is needed to check for errors and to make sure the machine is working as intended. This step prevents errors and material waste and ensures the final product meets the specifications.
Machining Operations
The machining operation is the actual cutting and shaping of the material, where the machine does the work. CNC machining includes:
Milling:
rotating cutting tools on a stationary workpiece.
Turning:
stationary cutting tool on a rotating workpiece.
Drilling:
(operation not described).
Electric discharge machines:
specialized machining process using electrical sparks (electrical discharges) between electrodes and a metal workpiece, with dielectric fluids, to shape metal parts.
Laser cutting:
precise thermal machining used in modern CNC systems for fast and accurate material removal.Each operation is determined by the machine and tooling.
Running the CNC program without human intervention is the machining operation. Matching the machining to the design complexity is key to getting the desired precision and functionality.
Types of CNC Machines

CNC machines come in many forms, each for a specific operation and application. The basic types of CNC machines are those that hold stock and the tool cuts and those that rotate stock and the tool cuts. Electronic machines are the most common in CNC systems today and can do intricate cuts and modifications with high accuracy.
These are categorized by their main function:- Milling
- Lathing
- Routing
- Cutting
- CNC routers: CNC routers are for complex computer controlled cutting tasks. They play a big role in automated manufacturing by allowing detailed and accurate cuts on various materials.
CNC Mills
CNC mills are multi tasking machines that use a 3 axis system to move the cutting tool along the X, Y and Z axes. This allows for many different milling operations to be performed making CNC milling machines suitable for many applications. The programming languages used for CNC mills are G-code or specialized languages to have precise control of the machining operations.
The first milling operation in CNC machining was plain milling which laid the foundation for face milling operations. Today CNC mills can do complex operations with high precision making them essential in modern manufacturing.
CNC Lathes
CNC lathes move a cutting tool around a spinning cylindrical workpiece, so they're perfect for making parts with the same design around their long axis. Key features include:
- Two axes, X and Z
- Can make complex designs not possible on manual machines
- G-code controlled so you have precise control over every move with a cnc lathe.
More advanced CNC lathes can handle non-cylindrical materials, so they're more versatile and can be used for more applications. Products made on CNC lathes include engine components, medical devices and consumer products that require high precision and consistency.
Plasma Cutters and Water Jet Cutters
Plasma cutters are great for cutting conductive materials with precision because they can generate high temperature plasma. Using a plasma torch, these cnc plasma cutters create plasma with compressed air gas and an electrical arc, clean cuts. Plasma cutters are good for cutting metals and other conductive materials, they are very useful in many industries.
Water jet cutters on the other hand use high pressure water to cut materials, they are good for a wider range of materials without causing heat damage. This versatility allows water jet cutters to cut delicate materials like composites and plastics with precision and clean cuts, waterjet cutting applications.
Materials Used in CNC Machining

CNC machining can make parts from many different materials, each chosen for the specific application. Here are some common metals:
Each metal has its own properties that makes them good for different applications.
Besides metals, CNC machining can work with plastics like ABS and PEEK, tough and
chemical resistant. Composite materials like carbon fiber reinforced plastics are
strong and light, good for aerospace and automotive applications.
The supplier's expertise in working with different materials makes a big difference in
the quality and performance of the parts.
Size Considerations in CNC Machining
When planning a CNC machining project the size of the part is a key factor that affects every stage of the process. CNC machines can handle parts of all sizes from tiny precision components for electronics to large structural parts for industrial equipment. But the size of your part will determine what type of CNC machine and cutting tools are best for the job.
For smaller parts compact CNC mills or mini CNC lathes will give you the precision and control for intricate details, while larger parts may require heavy duty CNC milling machines or specialized gantry style CNC equipment. The working envelope of the chosen cnc machine must be big enough to handle the stock material and allow for all the machining operations without compromising accuracy.
The size of the part also affects the selection of cutting tools. Smaller parts require fine high precision cutting tools to achieve tight tolerances, while larger parts may need robust longer cutting tools to remove more material. The machining strategy – tool paths, fixturing and setup – must be tailored to ensure stability and minimize vibration especially when working with oversized or unusual shaped workpieces.
Cost is another factor to consider. Machining very large parts can generate more waste and require more expensive CNC machines, while very small parts may require specialized equipment and extra setup time. By evaluating size requirements early in the design phase manufacturers can choose the right CNC machines and optimize the process for quality and cost.
In the end understanding size considerations in CNC machining will ensure your project is both possible and efficient and you get the parts you need.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CNC Machining
Understanding the benefits and drawbacks of CNC machining helps manufacturers make informed decisions. CNC machining has many benefits: precise control, high speed, quality. But there are also downsides: high cost of CNC machines and need for trained operators.
Weighing the pros and cons helps manufacturers determine if CNC machining is right for them, maximize benefits and minimize challenges.
Advantages
CNC machining has: Precise and repeatable production of complex parts, meets strict quality standards. High speed production of detailed and accurate cuts, increases productivity. Consistency meets high quality standards, good for large runs.
A big advantage of CNC machining is it can run continuously, minimizes downtime and increases productivity. With robust quality control, CNC machining is cost effective for many applications.
Disadvantages
Despite the many benefits, CNC machining has its downsides. One big disadvantage is the high cost of CNC machines, affects production budget and economics. These machines require big investment, not just on the initial purchase but also on maintenance and operational cost. High cost of CNC machines limits accessibility for small businesses or those with limited budget.
Another challenge is needing trained operators to ensure machining accuracy. Operator inexperience can cause errors in the CNC machining process, affects the final product's precision and quality. Wrong setup and programming can also produce unusable parts and material waste, increases cost and reduces efficiency.
Applications of CNC Machining
CNC machining is a good tool to have in many industries. Aerospace uses CNC machining to make engine parts, turbine blades and landing gear parts that need to be precise and reliable. Automotive uses CNC machining to make complex engine parts, cylinder heads and other critical parts.
Beyond aerospace and automotive, CNC machining is used in medical for custom implants and precise medical devices. Consumer products, electronics and machinery parts benefit from the precision and consistency of CNC machining. CNC machining can handle many materials so it's used in many industries and products.
Aerospace and Automotive
In aerospace, CNC machining is key to producing engine parts that are critical to performance and safety. Turbine blades, landing gear parts and other complex parts need the precision of CNC machining. CNC machining's reliability and accuracy means these critical parts meet strict quality standards which are essential for safety and efficiency of aircraft.
Similarly in automotive, CNC machining is used to produce high precision parts such as pistons, cylinder heads and complex body parts. The ability to produce these parts consistently and precisely is vital for performance and durability of vehicles. CNC machining's role in both aerospace and automotive highlights its importance in manufacturing and modern manufacturing.
Medical Devices and Consumer Products
Medical industry benefits from CNC machining particularly in producing highly customized implants and precise medical devices. These parts need exact specifications to fit individual patient anatomies and CNC machining provides the precision and customization. CNC machining's efficiency and accuracy also makes it ideal for producing medical devices that meet strict regulatory standards.
In consumer products, CNC machining is used to produce lightweight and durable housings for electronics and other parts that require high precision. The ability to produce consistent and reliable parts makes CNC machining a valuable tool in manufacturing various consumer goods, quality and performance.
Choosing the Right CNC Machining Service
Choosing the right CNC machining service is key to your manufacturing process. When choosing a service provider consider their expertise, the services they offer and the materials they can work with. You need to choose a provider that can meet your specific needs whether it's CNC milling, CNC routing or CNC turning.
Also look for a service provider that gives transparent cost estimation and breakdown of material and machining cost. This transparency helps in procurement planning and no hidden cost.
A good CNC machining service like Clarwe can boost your custom manufacturing and produce high quality parts.
Conclusion
CNC machining is a testament to how far technology has come in manufacturing, precision, efficiency and versatility. From the 1940s to today and across many industries, CNC machining has changed the way we produce complex and high quality parts. Understanding the process, components and benefits of CNC machining will allow you to get the most out of this technology.
As we have seen, CNC machining offers big advantages in precision, consistency and productivity, it's a must have in modern manufacturing. Yes it has its challenges like high cost and skilled operators but the benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. By choosing the right CNC machining service you can produce high quality parts that meet today's market demands. Join the future of manufacturing with CNC machining and unlock innovation and excellence.

